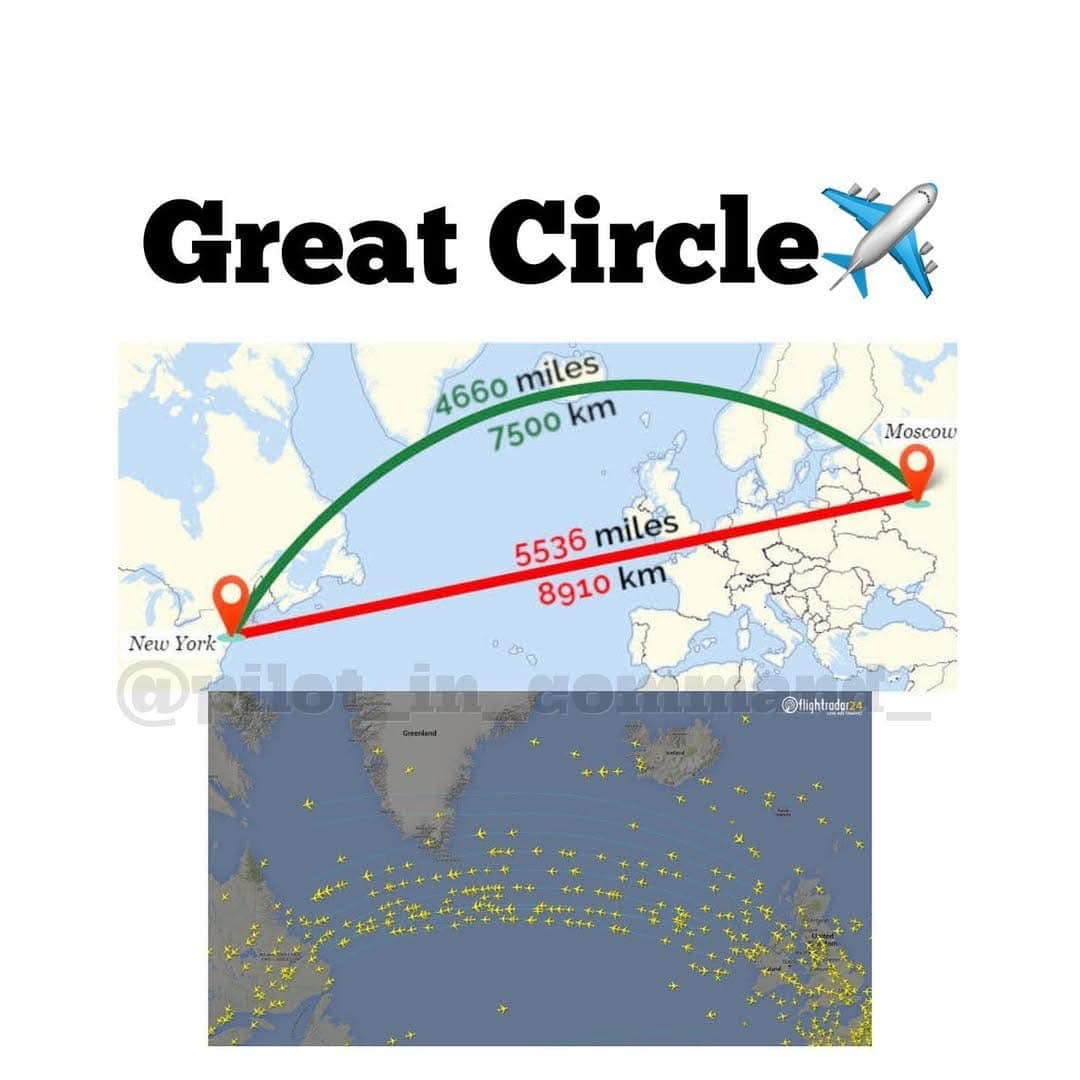
Great Circle Routes
A great circle route is the shortest distance between two points on the Earth's surface
“I have always preferred a 36,000-foot view.”
✈️ Planes Don’t Fly Straight Lines on Flat Maps
On a globe, the shortest path between two points is a great-circle route.
But on a flat map (like Mercator), that path looks curved.
A great circle route is the shortest distance between two points on the Earth's surface, appearing as a curve on flat maps but acting as a straight line (an arc) on a sphere. Used heavily in aviation and maritime navigation, these routes save fuel and time by following the circumference of the globe.
Key Aspects of Great Circle Routes:
Definition: A circle that cuts the Earth into two equal halves; meridians and the equator are examples.
Appearance: On a 2D Mercator projection, this path looks like a curve, often bending toward the poles.
Navigation: While it is the shortest path, it requires constant changes in compass heading, unlike a rhumb line (constant compass bearing).
Practicality: Airlines use these paths to maximize efficiency, with tools like gcmap.com visualizing these routes.
Deviations: Flights may not follow the perfect arc due to weather, jet streams, or geopolitical restrictions.